What is sterilisation?
Sterilisation is a permanent form of contraception that is intended to be non-reversible. It involves blocking the reproductive tubes to stop the ova (eggs) and sperm coming together.
Vasectomy
What is a vasectomy?
Vasectomy is a procedure that cuts the tube called the vas deferens so that sperm produced in the testes cannot get into the semen (cum). If there are no sperm in the semen then pregnancy cannot occur.
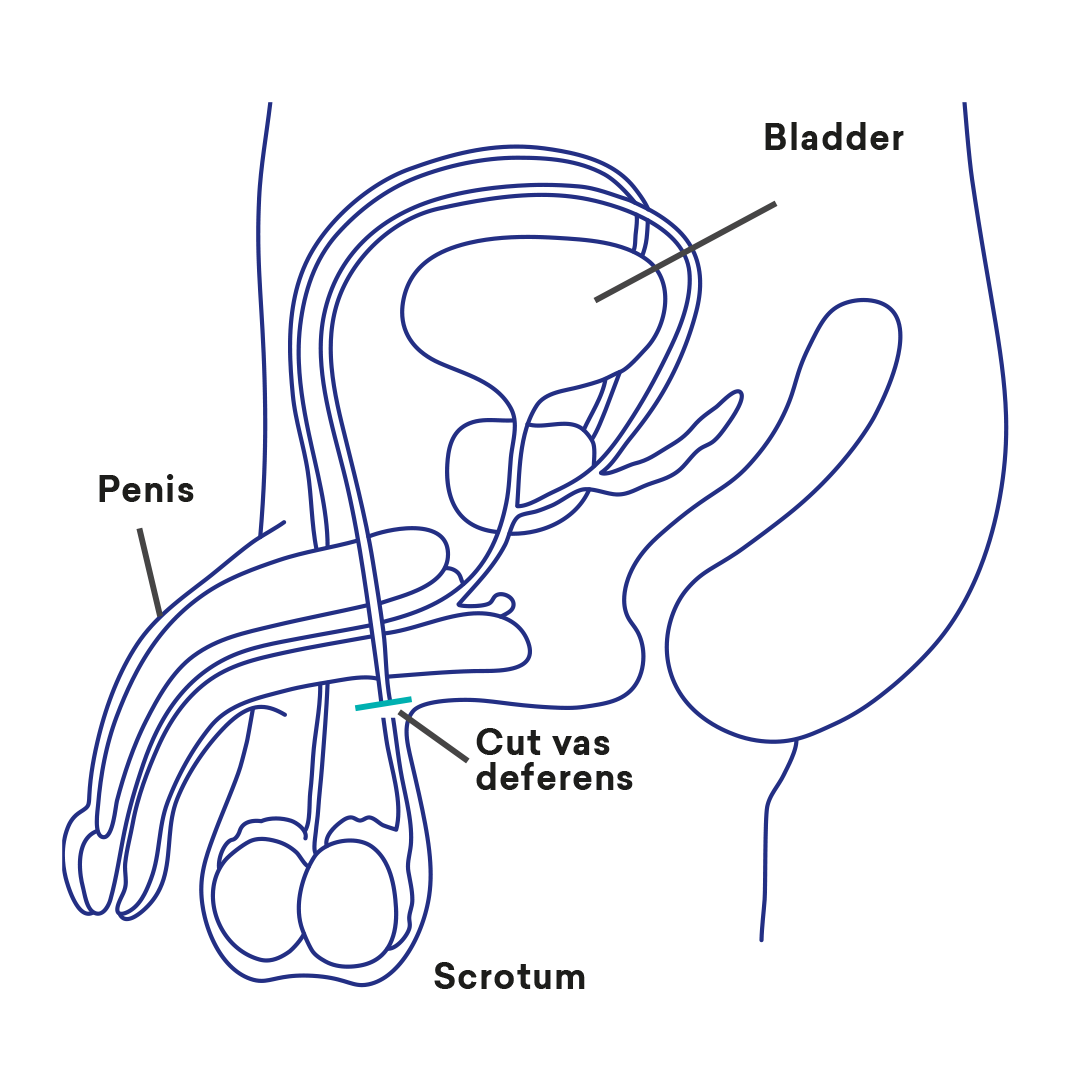
What happens during a vasectomy?
This procedure is done under local anaesthetic and doesn’t require an overnight stay. A small cut is made in the front of the scrotum so that the vas deferens can be located, cut and the ends sealed. The procedure takes about 15-30 minutes. This procedure can also be done under sedation.
How will I feel after a vasectomy?
When the anaesthetic wears off there will be some tenderness at the site of the operation. As with any procedure, complications can occur, but they are rare.
Discomfort and bruising can be reduced by simple pain-relieving medication, an ice pack and wearing underwear that supports the scrotum. Infection can usually be treated with oral antibiotics.
It’s important to rest for a few days after the procedure and avoid strenuous exercise as recommended.
Will I have any problems after the operation?
Longer-term complications can occur, such as pain lasting for more than 3 months; however, this is rarely severe.
There is no increased risk of testicular cancer and no reduction in testosterone (the hormone that is produced by the testes).
Does it work immediately?
After the procedure sperm will still be present in the tubes for up to 3 months. You should have a semen test after 12 weeks to see if all the sperm have gone.
Use another method of contraception until the semen test has confirmed that there are no sperm in your ejaculate (cum).
When can I have sex?
You can resume sexual activity after 2-3 days if you feel comfortable. The procedure will not change your sexual ability or enjoyment.
How effective is it?
It is very effective (99.5%). If the procedure has failed it can be picked up at the 12-week semen test.
How can I arrange a vasectomy?
A vasectomy can be done in public hospitals, by private specialists and by some general practitioners. For further information and referral if needed, see your doctor or SHINE SA.
How much does it cost?
There is no cost if you have a vasectomy in a public hospital. The cost of having this done privately depends on the clinic. Discuss this with your doctor.
Tubal Ligation
What is tubal ligation?
Tubal ligation is a procedure to block the fallopian tubes so that the sperm cannot reach the egg and begin a pregnancy.
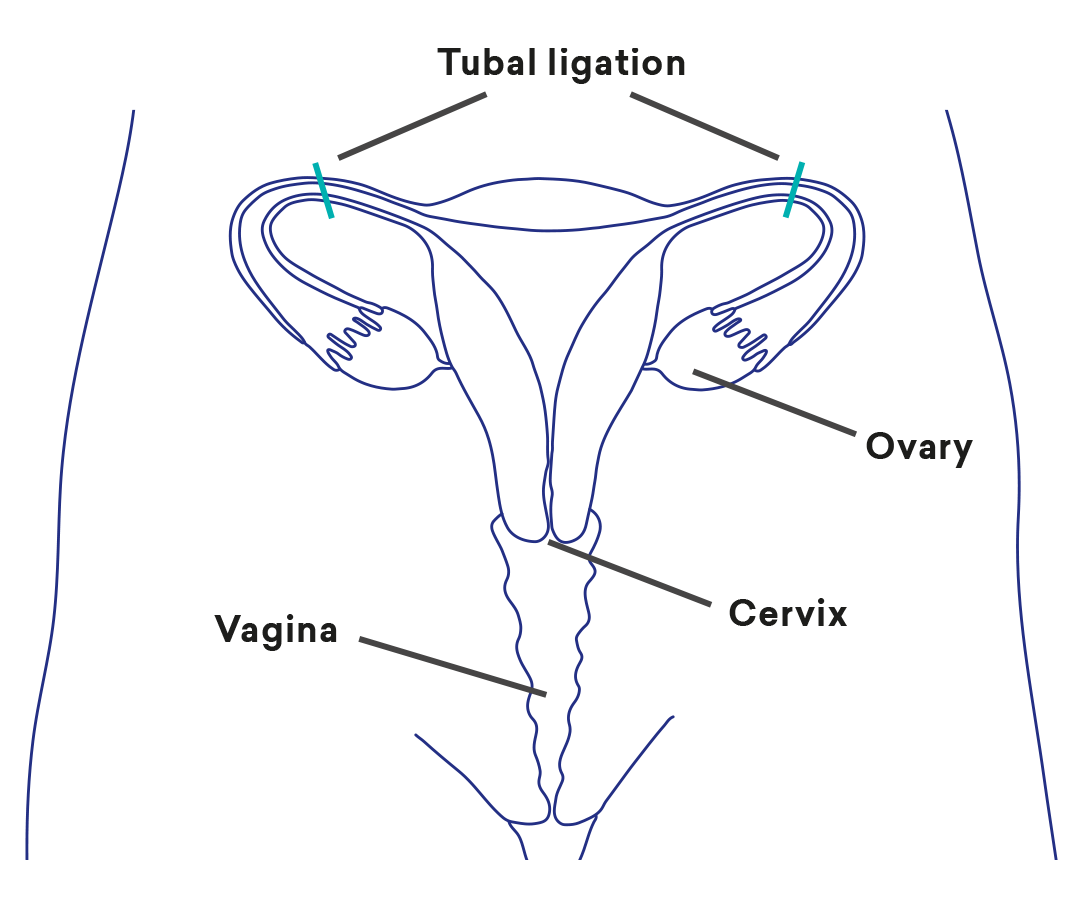
What is the procedure for tubal ligation?
You will need a general anaesthetic for this procedure. This is done as a laparoscopy (keyhole surgery), where a small telescope is inserted to find the fallopian tubes. The tubes are then closed off by clips or rings. For most people this is performed as day surgery.
How soon is the procedure effective?
The operation is effective immediately after the procedure, but contraception should be used right up to the time of the operation.
How effective is it?
Tubal ligation is very effective (99.5%). If a pregnancy does occur there is an increased chance of ectopic pregnancy (a pregnancy forming in the fallopian tube instead of the uterus).
What are the side effects?
The general anaesthetic can cause nausea or tiredness and the operation may cause some abdominal or shoulder pain. Painkillers can help but the pain can last for a couple of days. Serious complications are rare but can include excessive bleeding, infection, and injuries to bowel and bladder.
After a laparoscopy it’s important to rest for a few days and avoid strenuous exercise for the first week.
You can have sex as soon as you feel comfortable. The procedure will not change your sexual ability or enjoyment.
Will I have any problems after the tubal ligation?
Periods and menopause are not affected by tubal ligation. It also has no direct effect on sexual intercourse or sexual desire. If you are using hormonal contraception you may experience a change to your bleeding when you stop. This is not caused by the procedure, it is a return to your natural cycle.
How can I arrange a tubal ligation?
A tubal ligation can be done in public hospitals or by private specialists. You will need a referral from a GP.
How much does tubal ligation cost?
There is no charge in public hospitals; however, there is a waiting list. Private hospitals charge a fee for hospital stay, surgery and anaesthetic.
Can sterilisation be reversed?
It is sometimes possible to restore the vas deferens or fallopian tubes but it involves complex surgery and is not always successful. The success rate depends on the type of procedure, the age of the person at the time of reversal and the amount of time since the sterilisation procedure occurred. It is not available in public hospitals and Medicare rebates don’t apply for private reversal.
It is really important to think of sterilisation as permanent and discuss the consequences of sterilisation with your partner/s and health professionals before the procedure.
In general vasectomy is a safer procedure than tubal ligation with less complications and may be easier to access.
Long Acting Reversible Contraceptive (LARC) methods, such as IUDs and implants, are also available and may be a good option for people who are not ready for permanent contraception.
Sterilisation does not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs) or blood-borne viruses (BBVs). Practise safer sex. Condoms reduce the risk of STIs and BBVs.






